Data Annotation for Autonomous Cars & Self Driving Vehicle




Need of data annotation in self driving vehicles
Self driving capabilities & ADAS features depend on the robustness of the AI algorithms & machine learning models which need to make informed decisions for navigation, road planning, and overall safety. To achieve safety clearance, self driving systems must run thousands of miles without any incidents. For a computer vision model, it needs to be trained with high-quality annotated and labeled training data.
How is data labeling used for autonomous vehicles?
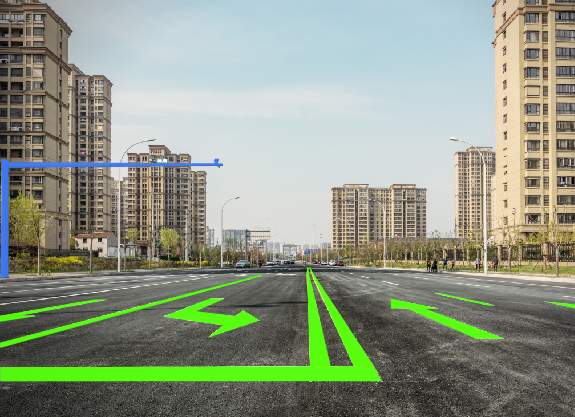
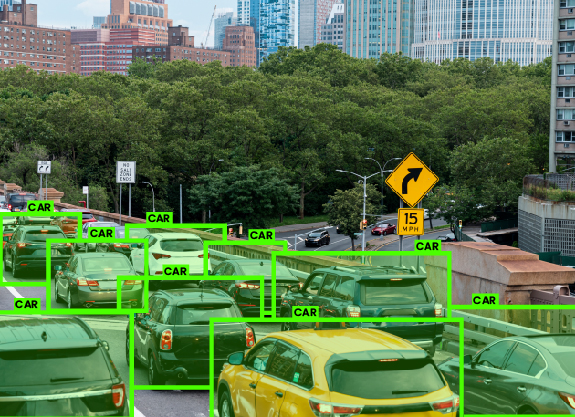

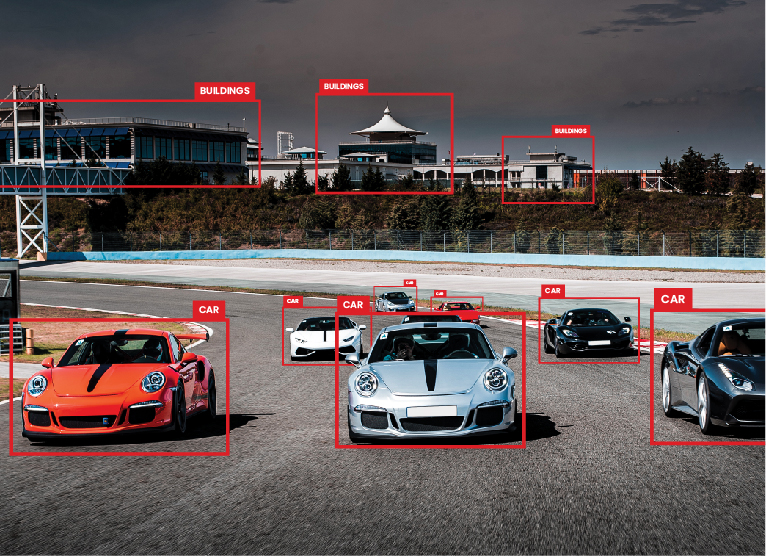
Bounding boxes for identification of objects such as different cars on road

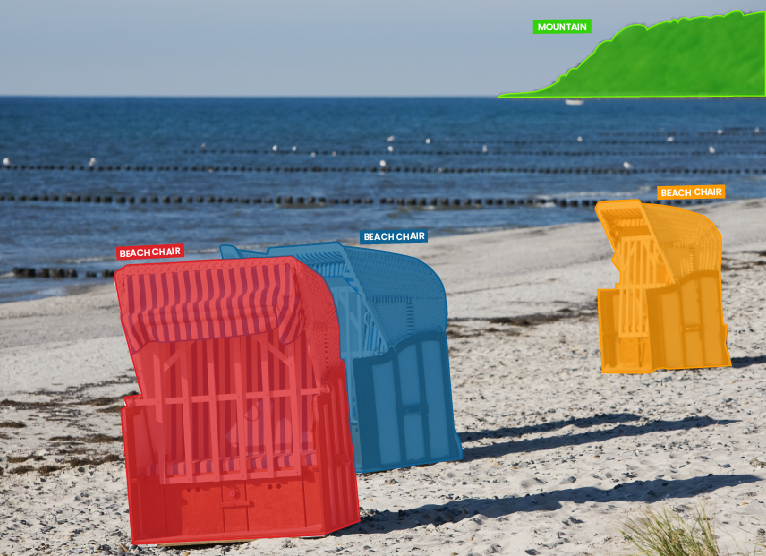
Polygon annotation for classifying exact edges of all the objects including irregular shapes
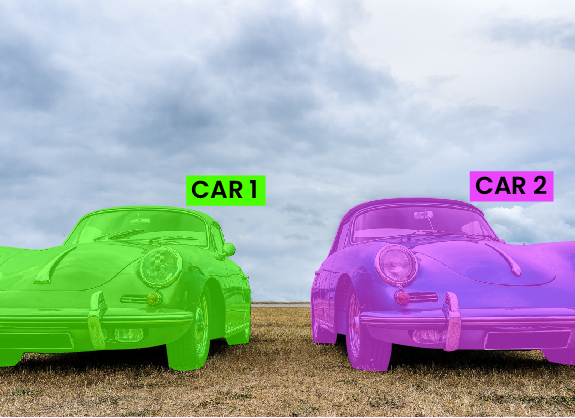

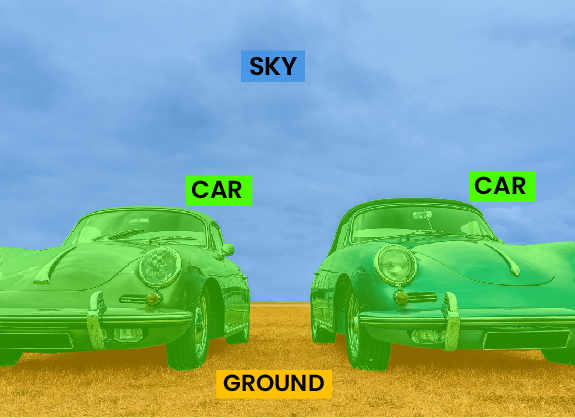
Panoptic segmentation to label each pixel of each object in different classes as Car 1, Car 2

Semantic segmentation to label each pixel of different object classes such as cars and sky
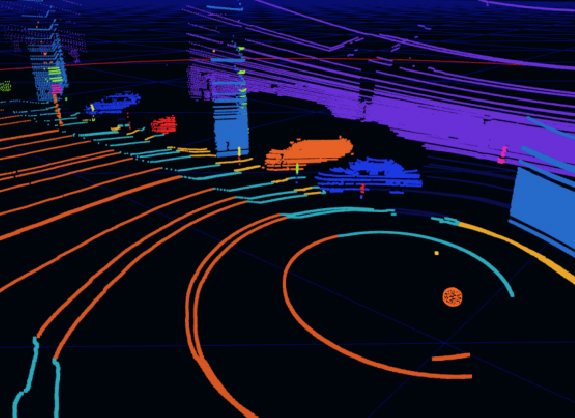

3D LiDAR Point Cloud for LiDAR annotation to get accuracy up to 1cm

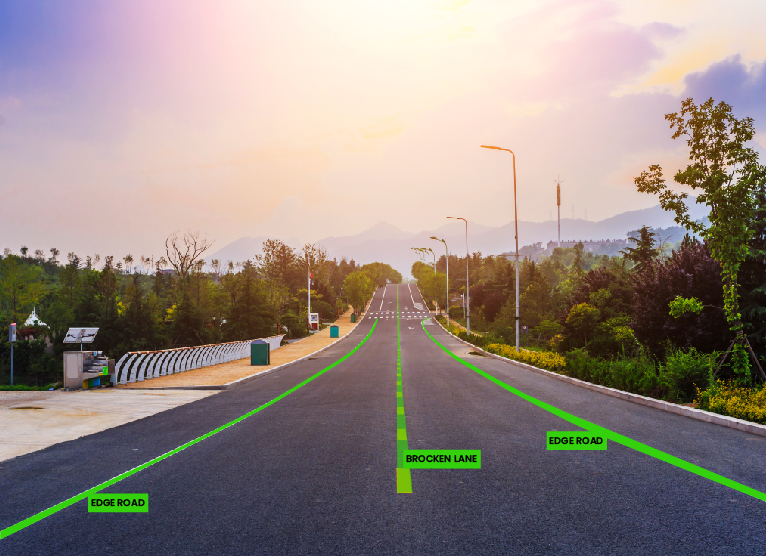
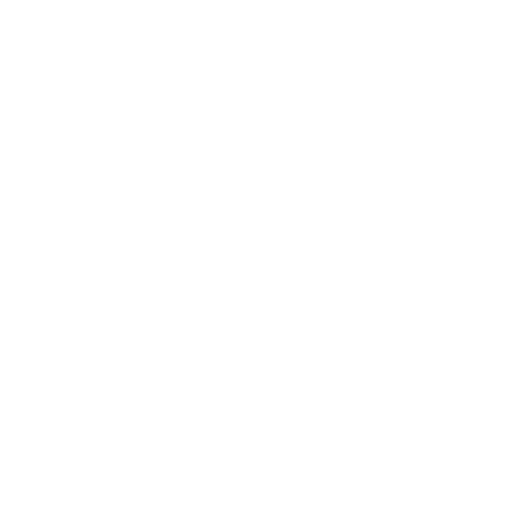
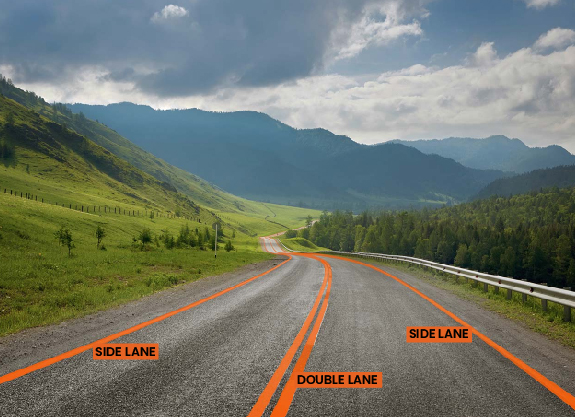
Polyline annotation to assist in lane detections
Annotation tools used in Automobile industry
Look no further! Let our subject matter experts take care of your data annotation and labelling needs.
Our beliefs behind each annotations

Data Security & Privacy

Fast Delivery with High Accuracy

Cost Effective Pricing

Scalable Solution by Experts
- We are EU-GDPR compliant and SOC 2 Type 1 organization. Data security & privacy is non-negotiable for us
- Our scalable annotation solutions are driven by specialists with years of experience in AI & ML
- We deliver fast and achieve 95%+ accuracy in our annotations
- We aim to achieve highest client satisfaction while providing low cost annotation and fostering longterm relations
LIDAR sensors work by emitting laser pulses and then waiting for their reflection to measure the time it takes them to fly from and back to the sensor. The flight time is then used to calculate the distance between the object and the sensor. The LIDAR sensors can also measure the height of the vegetation around them based on the same principle.
LiDAR is implemented for various purposes, including in autonomous vehicles, land management and planning efforts, hazard assessment in landslides, tsunamis, floods, geologic mapping, agriculture, and river surveys. Lidar is also finding applications among the police in speed limit enforcement, 3D crime, accident recording, and blood splatter analysis.
The light pulses emitted by the LIDAR sensors are invisible to the human eyes by can be seen using a night vision camera. The light wave emitted is similar to sonar waves. A Lidar system includes a laser that produces and emits. It records ground and back flight time, the GPS receiver that identifies the light energy’s X, Y, and Z location, and an IMU scanner that provides the plane’s orientation in the sky.
LIDAR imaging is a technology used in the creation of high-resolution models of ground elevation with a vertical accuracy of 4 inches. The technology uses laser light pulses to densely sample the earth’s surface to produce a highly accurate representation. The elevation of the ground, canopy, highway overpasses and buildings encountered during the survey is then used to constitute the point cloud data.
LIDAR scanning is a LIDAR application used to examine the earth’s surface to collect and assess information about the ground surface, provide detailed geospatial data, or create digital clones of objects on the earth’s surface. Lidar scanning helps create 3D models of the earth’s surface and digitally determine elevation.
Point of cloud data is a set of data points in space collected for specific terrain, buildings, or geographical area. Point cloud data is stored by grouping together point records with common Lidar scan locations or those with common spatial relationships. An example of point cloud data is data generated by scanning an area with LIDAR.